Auto Immune and Genetic Diseases Non-Invasive Diagnosis and Therapy
|
|
|
|
NON-INVASIVE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT FOR AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS
A disease in which the body's immune system attacks healthy cells. An autoimmune disease is a condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body.
The immune system normally guards against germs like bacteria and viruses. When it senses these foreign invaders, it sends out an army of fighter cells to attack them. Normally, the immune system can tell the difference between foreign cells and your own cells. In an autoimmune disease, the immune system mistakes part of your body - like your joints or skin - as foreign. It releases proteins called autoantibodies that attack healthy cells.
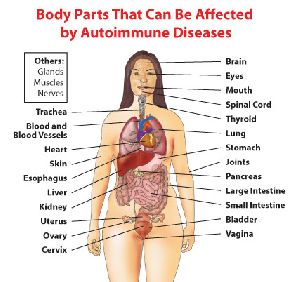
Some autoimmune diseases target only one organ. Type 1 diabetes damages the pancreas. Other diseases, like lupus, affect the whole body.
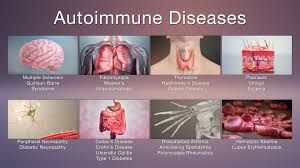
Most common types
Addison’s disease
- Addison’s disease affects the adrenal glands, which produce the hormones cortisol and aldosterone. Having too little of these hormones can affect the way the body uses and stores carbohydrates and sugar.
- Symptoms include weakness, fatigue, weight loss, and low blood sugar.
Alopecia areata :
- Sudden hair loss that starts with one or more circular bald patches that may overlap.
Ankylosing spondylitis :
- An inflammatory arthritis affecting the spine and large joints.
Celiac disease
People with celiac disease can’t eat foods containing gluten — a protein found in wheat, rye, and other grain products. When gluten is in the intestine, the immune system attacks it and causes inflammation.
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Similar to Guillian-Barre, the immune system also attacks the nerves in CIDP, but symptoms last much longer. About 30% of patients can become confined to a wheelchair if not diagnosed and treated early. Treatment for CIDP and GBS are essentially the same.
Graves' disease
The immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to release excess amounts of thyroid hormone into the blood (hyperthyroidism). Symptoms of Graves' disease can include bulging eyes as well as weight loss, nervousness, irritability, rapid heart rate, weakness, and brittle hair. Destruction or removal of the thyroid gland, using medicines or surgery, is usually required to treat Graves' disease.